What is Antimatter ?
Antimatter:
Antimatter is defined as matter which is composed of the antiparticles (or "partners") of the corresponding particles of 'ordinary' matter. Minuscule numbers of antiparticles are generated daily at particle accelerators – total production has been only a few nanograms and in natural processes like cosmic ray collisions and some types of radioactive decay, but only a tiny fraction of these have successfully been bound together in experiments to form anti-atoms. No macroscopic amount of antimatter has ever been assembled due to the extreme cost and difficulty of production and handling.
In theory, a particle and its anti-particle have the same mass, but opposite electric charge and other differences in quantum numbers. For example, a proton has positive charge while an antiproton has negative charge.
A collision between any particle and its anti-particle partner leads to their mutual annihilation, giving rise to various proportions of intense photons (gamma rays), neutrinos, and sometimes less-massive particle-antiparticle pairs. The majority of the total energy of annihilation emerges in the form of ionizing radiation. If surrounding matter is present, the energy content of this radiation will be absorbed and converted into other forms of energy, such as heat or light. The amount of energy released is usually proportional to the total mass of the collided matter and antimatter, in accordance with the mass–energy equivalence equation, E=mc2
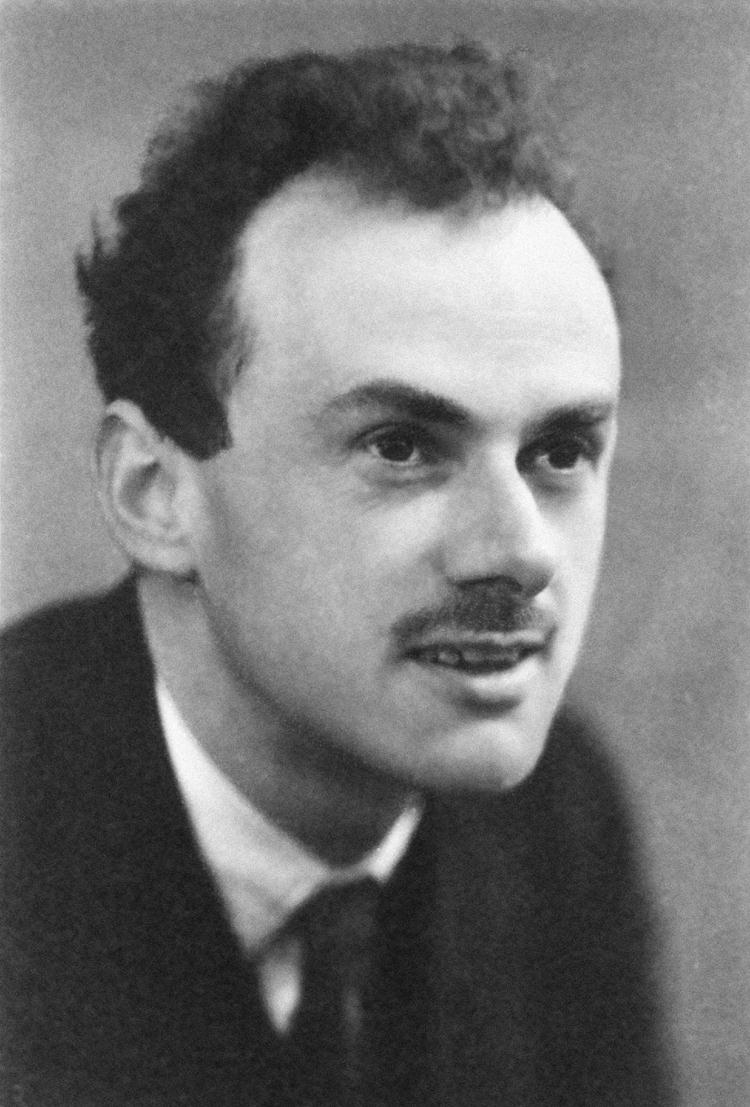
Antimatter was first predicted in 1928 by English physicist Paul Dirac, who New Scientist magazine called "the greatest British theorist since Sir Isaac Newton."
Dirac put together Einstein's special relativity equation (which says light is the fastest-moving thing in the universe) and quantum mechanics (which describes what happens in an atom), according to the magazine. He discovered the equation worked for electrons with negative charge or with positive charges.
While Dirac was at first hesitant about sharing his findings, he eventually embraced them and said that every particle in the universe would have a mirror image. American physicist Carl D. Anderson discovered positrons in 1932. Dirac received a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933, and Anderson got the prize in 1936.
Properties:
Theorized anti-gravitational properties of antimatter are currently being tested at the alpha experiment at CERN .Antimatter coming in contact with matter will annihilate both while leaving behind pure energy. Research is needed to study the possible gravitational effects between matter and antimatter, and antimatter and antimatter. However research is difficult considering when the two meet they annihilate, along with the current difficulties of capturing and containing antimatter
Cost:
Scientists claim that antimatter is the costliest material to make.In 2006, Gerald Smith estimated $250 million could produce 10 milligrams of positrons in 1999, NASA gave a figure of $62.5 trillion per gram of antihydrogen. This is because production is difficult and because there is higher demand for other uses of particle accelerators. According to CERN, it has cost a few hundred million Swiss francs to produce about 1 billionth of a gram . In comparison, to produce the first atomic weapon, the cost of the Manhattan Project was estimated at $23 billion with inflation during 2007.


Comments
Post a Comment